Sweet fennel
Scientific name|Foeniculum vulgare
Origin|Spain
Classification|Herb series
Specifications|500g-25kg Please contact sales for details
Extraction part|Seed
Extraction method | Distillation
Plant family|Apiaceae
Aroma|With a hint of spiciness, the aroma features floral and herbal notes
▎Essential Oil Introduction
Sweet fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) is native to the Mediterranean coast of Southern Europe. It is a perennial plant from the Apiaceae family that thrives in sunny, well-drained areas and is highly adaptable to various environments. It is now widespread across Europe, India, China, and North America.
Sweet fennel has a long history of use. In ancient times, it was used by warriors to enhance courage and strength. It also symbolizes commitment, helping to keep lifelong promises between married partners. The medicinal and culinary use of fennel dates back to ancient Egypt, where the Greeks discovered its diuretic properties, and the Romans used it to aid digestion and freshen breath.
In addition to its digestive benefits, sweet fennel is also valued by women. It contains trans-anethole, which is effective for alleviating discomfort during menstruation or menopause and is commonly used in Indian gynecological treatments.
▎Component Analysis
|Main component: Ethers
The typical main component of sweet fennel is trans-anethole (a phenyl ether), which constitutes approximately 66%-77% of the oil. Additionally, it contains various trace components, including methyl chavicol, 1.8-cineole, α-pinene, limonene, fenchol, fennel ketone, camphor, anethole, and furanocoumarins.
|Component 1: Anethole
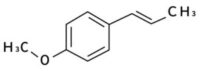
▸ Also known as propenylphenol, is a plant-based phytoestrogen available in both cis and trans forms.
|Component 2: Methyl chavicol
Also known as estragole, fenchol is a major component of tarragon essential oil. It is an isomer of anethole, with the difference being the position of the double bond in the phenylpropyl group. While they have similar effects, their aromas are distinct.
This component constitutes approximately 80% of tarragon essential oil, about 85% of tropical basil essential oil, and around 90% of aromatic rosemary leaf oil (extracted from the peel).
|Raw Material Certifications
To obtain relevant certification information, please contact us on WhatsApp.
▎References
- Coelho-de-Souza AN, Lahlou S, Barreto JEF, Yum MEM, Oliveira AC, Oliveira HD, Celedônio NR, Feitosa RGF, Duarte GP, Santos CF, de Albuquerque AAC, Leal-Cardoso JH. Essential oil of Croton zehntneri and its major constituent anethole display gastroprotective effect by increasing the surface mucous layer. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2013;27:288-298.
- Ibrahim AM, Mohamed AS, Saleh A, Mansour AS, Mohammed AD, Mohamed AY et al. Fennel “Foeniculum vulgare” treatment protects the gastric mucosa of rats against chemically-induced histological lesions. Int J Pharmacol. 2013;9:182 -189.
- Birdane FM, Cemek M, Birdane YO, Gülçin İ, Büyükokuroğlu ME. Beneficial effects of Foeniculum vulgare on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(4):607-611.
- Dhar SK. Anti-fertility activity and hormonal profile of trans-anethole in rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995;39:63-67.
- Minnema DJ. 90-Day subchronic dietary toxicity study of trans-anethole in mice. 1997, CHV2595- 103. Corning Hazletone Inc. Vienna, VA.
- Oktay M, Gülcin I, Küfrevioglu O. Determination of in vitro antioxidant activity of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) seed extracts. Lebensm Wiss Technol. 2003;36:263-271.
- Astani A, Reichling J, Schnitzler P. Screening for antiviral activities of isolated compounds from essential oils. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;253643:1-8.
- Maruzzella J, Freundlich M. Antimicrobial substances from seeds. J Am Pharm Assoc. 1959;48:356-358.
- Veselin Marinov, Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova. REVIEW ON THE PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF ANETHOLE. Department of Preclinical and Clinical Pharmacology, Medical University of Varna
- Bernáth, J. et al. 1998. Production-biological and structural regularities of essential oil accumulation in developing fruits of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare Mill.). Budapest: UHFI Department of Medicinal Plant Production.
- Bown, D. 1995. Encyclopedia of Herbs and Their Uses. New York: DK Publishing, Inc. 283-284.
- British Herbal Pharmacopoeia (BHP). 1996. Exeter, U.K.: British Herbal Medicine Association.
- Bruneton, J. 1995. Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Medicinal Plants. Paris: Lavoisier Publishing.
- Deutsches Arzneibuch, 10th ed. (DAB 10). 1991. (With subsequent supplements through 1996.) Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag.
- ESCOP. 1997. 'Foeniculi aetheroleum' and 'Foeniculi fructus.' Monographs on the Medicinal Uses of Plant Drugs. Exeter, U.K.: European Scientific Cooperative on Phytotherapy.
- Europäisches Arzneibuch, 3rd ed. (Ph.Eur.3). 1997. Stuttgart: Deutscher Apotheker Verlag. 939-941.
- Grieve, M. 1979. A Modern Herbal. New York: Dover Publications, Inc.
- Karnick, C.R. 1994. Pharmacopoeial Standards of Herbal Plants, Vols. 12. Delhi: Sri Satguru Publications. Vol. 1:139141; Vol. 2:71.
- Lange, D. and U. Schippmann. 1997. Trade Survey of Medicinal Plants in GermanyA Contribution to International Plant Species Conservation. Bonn: Bundesamt für Naturschutz. 32-33.
- Leung, A.Y. and S. Foster. 1996. Encyclopedia of Common Natural Ingredients Used in Food, Drugs, and Cosmetics, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Nadkarni, K.M. 1976. Indian Materia Medica. Bombay: Popular Prakashan. 557-559.
- Ph.Eur.3. See Europäisches Arzneibuch.
- Österreichisches Arzneibuch, Vols. 12, 1st suppl. ( AB). 1981-1983. Wien: Verlag der Österreichischen Staatsdruckerei.
- Tanira, M.O.M. et al. 1996. Pharmacological and toxicological investigations on Foeniculum vulgare dried fruit extract in experimental animals. Phytother Res 10:33-36.
- Tu, G. (ed.). 1992. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China (English Edition 1992). Beijing: Guangdong Science and Technology Press. 70.
- Wichtl, M. and N.G. Bisset (eds.). 1994. Herbal Drugs and Phytopharmaceuticals. Stuttgart: Medpharm Scientific Publishers.
|Some images sourced from the internet. Contact for copyright removal|