Roman Chamomile
Scientific name|Chamaemelum nobile
Origin|Bulgaria
Classification|Flower series
Specifications|500g-25kg Please contact sales for details
Extraction part|Flower
Extraction method | Distillation
Plant family|Asteraceae
Aroma|Refreshing floral scent similar to apples
▎Essential Oil Introduction
Roman chamomile has a scent similar to apples, which is why its name comes from the Greek word chamaimelon, meaning "apple of the ground." It blooms from June to July and is an annual herbaceous plant that grows to a height of 50-70 cm. Unlike German chamomile, Roman chamomile has a lower yellow central disc. Perennial varieties of Roman chamomile grow as low, ground-covering plants, and are often called the "plant doctor" because plants grown nearby tend to be healthier. It's believed that the secretions from its roots help rejuvenate nearby plants.
There are many varieties of Roman chamomile, including double-flowered types, which have been cultivated since 1932 and are used as chamomile lawns in Buckingham Palace gardens. In the book Plant Personality (by Wen, You-Jun), Roman chamomile is classified as having a "caregiver personality" because of its esters, which convey "love and support." This plant is associated with the nurturing, protective love of a parent and provides a sense of primal security. It is especially effective in balancing emotions, making it useful for soothing those who are emotionally fragile, lack a sense of security, are easily hurt, or tend to overinterpret situations.
▎Component Analysis
|Main component: Esters
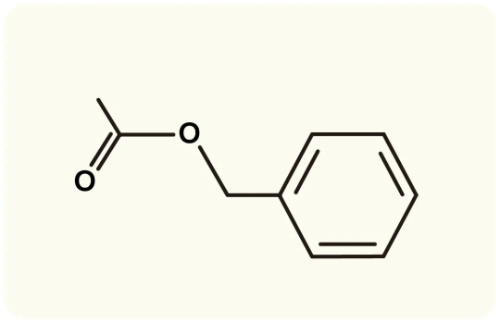
▸ Its main components include limonene, α-pinene, and carvone, which give Roman chamomile a slightly grassy scent. These compounds also make it effective in relieving congestion and stagnation. Although Roman chamomile contains a small amount of ketones, it does not pose a neurotoxic risk when used correctly. It is one of the most widely used essential oils in aromatherapy.
|Other component: Isobutyl angelate
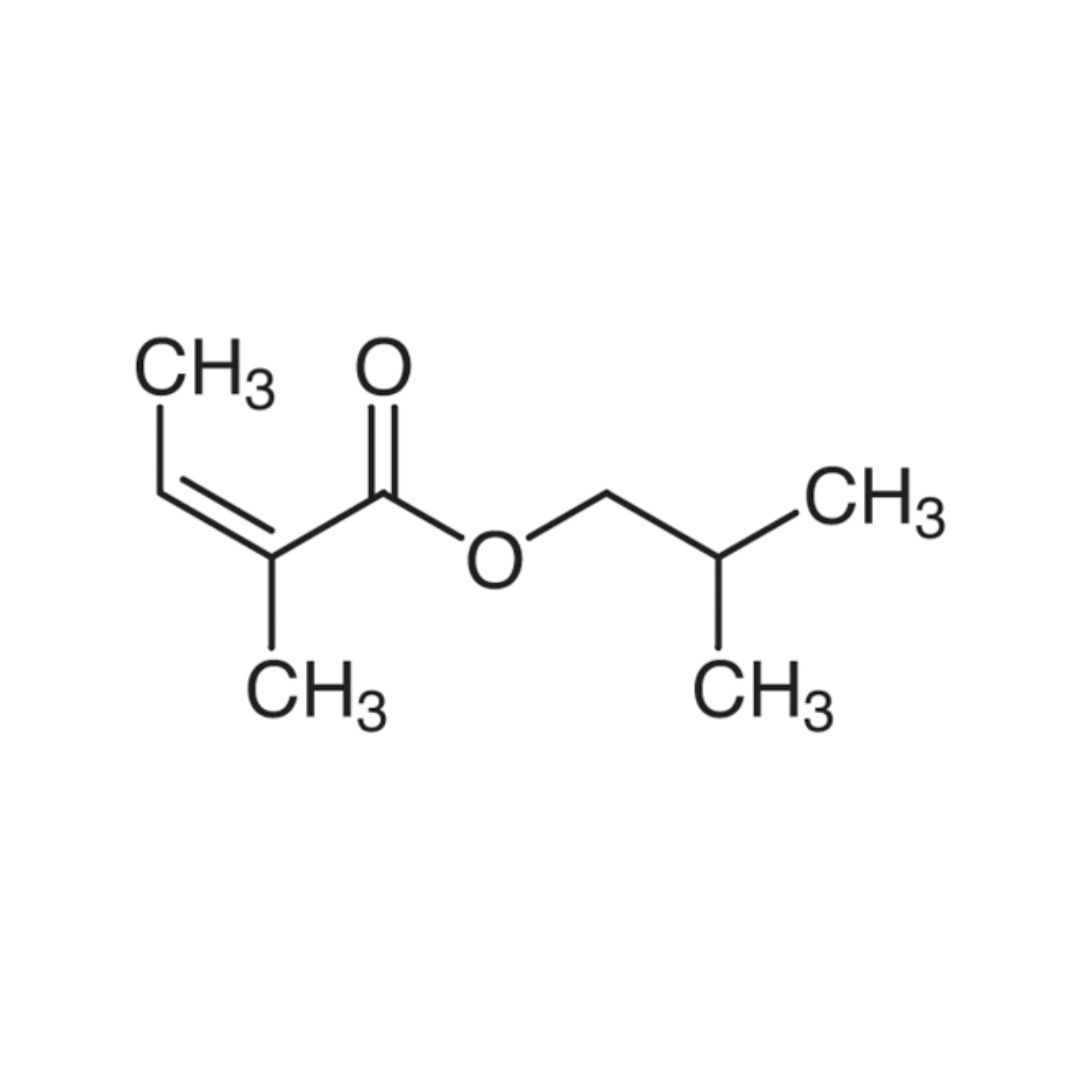
▸ Isobutyl angelate, is a compound where "Isobutyl" refers to its origin from isobutanol, and "angelate" comes from angelic acid. Along with isopentyl angelate, it belongs to the rare class of fatty acid esters within the ester group of essential oils. This compound is a key contributor to the apple-like scent of Roman chamomile, making up over 75% of its content.

▸ GC/MS analysis identified isobutyl angelate and 2-methylbutyl isobutyrate as the main components of Roman chamomile. These compounds significantly enhanced the activity of mice, confirming them as the primary active ingredients in Roman chamomile essential oil (CHA). The study also showed that these active components have similarities with the neurotransmitter dopamine.
|Raw Material Certifications
To obtain relevant certification information, please contact us on WhatsApp.
▎References
- Zsolt Sándor1,el. Evidence Supports Tradition: The in Vitro Effects of Roman Chamomile on Smooth Muscles. Published online 2018 Apr 6.
- Toyoshi Umezu.Identification of isobutyl angelate, isoamyl angelate and 2‐methylbutyl isobutyrate as active constituents in Roman chamomile essential oil that promotes mouse ambulation.
- EMA-HMPC (2012). Community Herbal Monograph on Chamaemelum nobile (L.) All., Flos. London: EMA-HMPC.
- Kazemian H1, Ghafourian S1, Heidari H2. Antibacterial, anti-swarming and anti-biofilm formation activities of Chamaemelum nobile against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2015 Jul-Aug;48(4):432-6.
- Menendez-Baceta G., Aceituno-Mata L., Molina M., Reyes-García V., Tardío J., Pardo-de-Santayana M. (2014). Medicinal plants traditionally used in the northwest of the Basque Country (Biscay and Alava), Iberian Peninsula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 152 .113–134.
- Alarcün R., Pardo-de-Santayana M., Priestley C., Morales R. (2015). Author’s accepted manuscript. J. Ethnopharmacol. 176. 207–224.
- Janmejai K Srivastava,1,2,* Eswar Shankar,1,2 and Sanjay Gupta1,2, Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future. Mol Med Report. 2010 Nov 1; 3(6): 895– 901.doi: 10.3892/mmr.2010.377
- Essential Oils: A Handbook for Aromatherapy Practice Second Edition. Genus Anthemis Anthemis Nobilis(Also Known As Chaemamelum Nobile)-Roman Chamomile.145-146
- Hernández-Ceruelos A., Madrigal-Santillán E., Morales-González JA, Chamorro-Cevallos G., Cassani-Galindo M., Madrigal-Bujaidar E. (2010). Antigenotoxic effect of Chamomilla recutita (L.) rauschert essential oil in mouse spermatogonial cells, and determination of its antioxidant capacity in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11:3793–3802.
- Zeggwagh N. A., Moufid A., Michel J. B., Eddouks M. (2009). Hypotensive effect of Chamaemelum nobile aqueous extract in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 31: 440–450.
- Effect of the Internal and External Factors on Yield and Qualitative-Quantitative Characteristics of Chamomile Essential Oil. Acta horticulturae: June 2007, Volume: 749
- Adams R. P. (2007). Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy.
- Barthó L., Benkó R., Patacchini R., Pethö G., Holzer-Petsche U., Holzer P., et al. (2004). Effects of capsaicin on visceral smooth muscle: a valuable tool for sensory neurotransmitter identification . Eur. J. Pharmacol. 500: 143–157.
- Antonelli A., Fabbri C. (1998). Study on Roman chamomile Chamaemelum nobile L. all. oil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 10: 571–574.
- Melegari M., Albasini A., Pecorari P., Vampa G., Rinaldi M., Rossi T., et al. (1988). Chemical characteristics and pharmacological properties of the essential oils of Anthemis nobilis. Fitoterapia 59: 449 –455.
- Abou-Zied E., Rizk A. (1973). Phytochemical investigation of Anthemis nobilis L. growing in Egypt. Qual. Plant. Mater. Veg. 2: 141–144.
- Augustin B., Javorka S., Giovannini R. R. P. (1948). Magyar Gyógynövények [Hungarian Herbal Drugs. New Delhi: Ministry of Agriculture, 299–300.
|Some images sourced from the internet. Contact for copyright removal|