羅馬洋甘菊 Roman Chamomile
拉丁學名|Chamaemelum nobile
主要產地|保加利亞
原料分類|花朵系列
原料規格|500g-25kg 詳情請洽業務
萃取部位|花朵
萃取方式|蒸餾
植物科別|菊科
植物氣味|類似蘋果的清爽花香味
▎精油簡介
羅馬洋甘菊擁有類似蘋果的香氣,因此名稱源自於希臘chamaimelon,地上的蘋果之意,6-7月開花,草長50-70cm,1年生草本植物,和德國洋甘菊外觀不同在於,黃色花蕊較低。多年生的羅馬洋甘菊是低矮的地披植物,是植物醫生,只要種在羅馬洋甘菊附近的植物,都較少生病,據說它的根系分泌的植物,可以幫助附近植物恢復生氣。
羅馬洋甘菊有很多品種,包括重瓣品種,它從1932年就培育出來作為白金漢宮花園當中的洋甘菊草皮。在《植物人格全書》羅馬洋甘菊歸入「照顧者人格」,因為酯類具有「愛與支持」,而且是如同父母般無微不至的家人之愛,是原始安全感的來源。所以它特別具有情緒平衡的功效,適用於安撫那些內心脆弱、缺乏安全感、容易受傷,對遭遇的事物過度詮釋的人。
▎成分解析
|主要成分:酯類
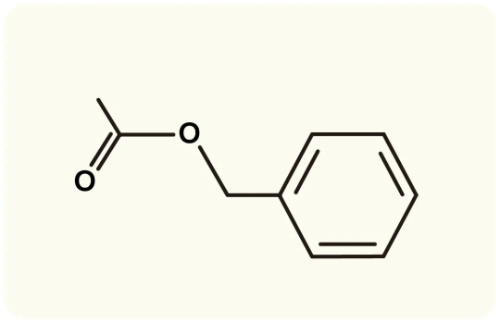
▸ 其成分主要有,另外有檸檬烯(limonene)、α-蒎烯(pinene),以及松香芹酮(carvone)(使羅馬洋甘菊散發些許帶有青草味),也是化解瘀塞凝滯的高手。雖然羅馬洋甘菊含有微量酮,在正確使用下不會造成神經毒性的問題,在芳香療法中,是最被廣泛運用的精油。
|成分:歐白芷酸異丁酯(Isobutyl angelate)
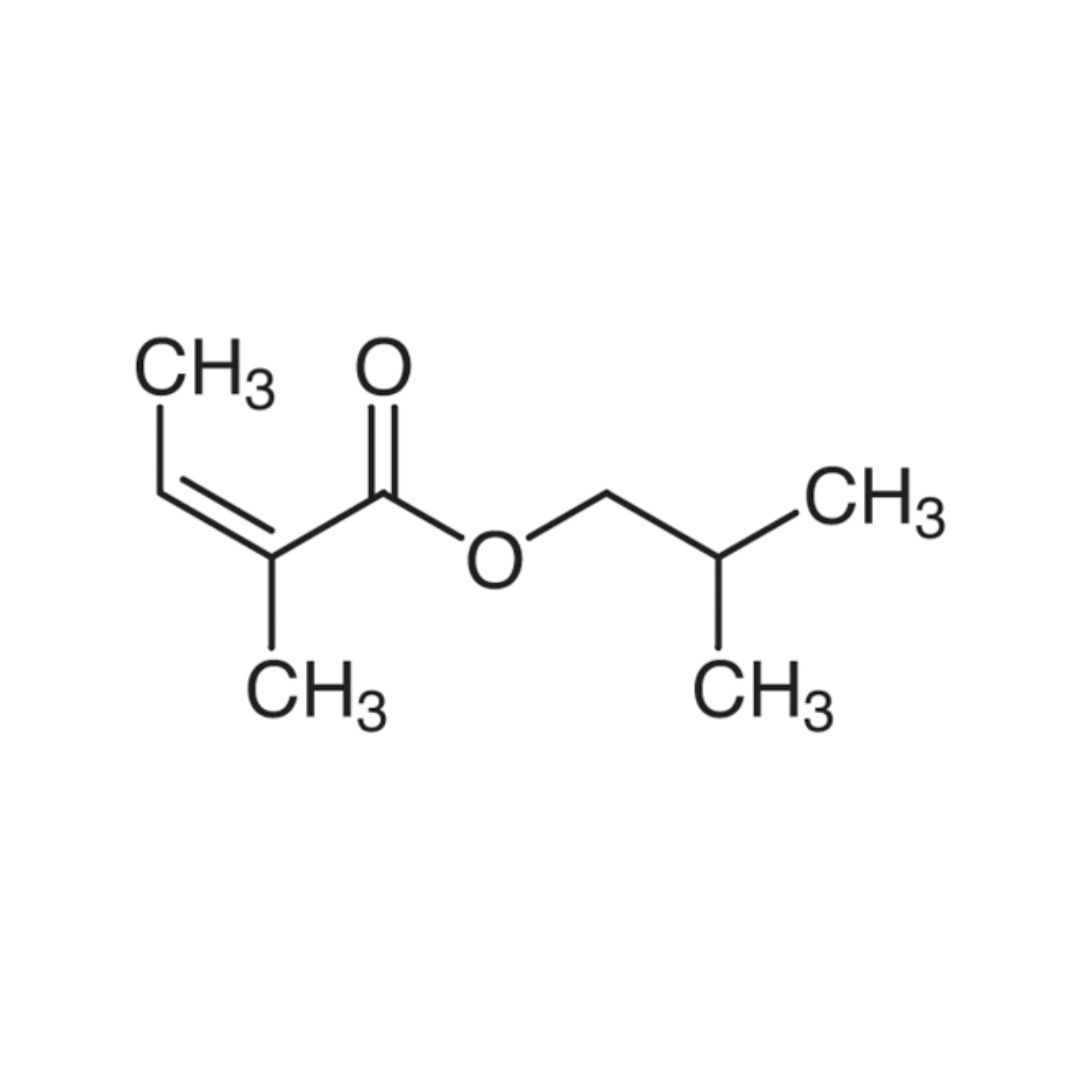
▸ 甲基戊二酸酯(Isobutyl angelate)或稱當歸酸異丁酯,「Isobuty」表示來自異丁醇,「angelate」來自歐白芷酸,和歐白芷酸異戊酯,再精油是屬於酯類中罕見的脂肪酸類,也是讓羅馬洋甘菊散發蘋果香氣的成分,其含量高達75%以上。

▸ 從GC/MS分析出歐白芷酸異丁酯(Isobutyl angelate),歐白芷酸異戊酯(Isoamyl angelate)和異丁酸2-甲基丁酯(2‐methylbutyl isobutyrate)是羅馬洋甘菊的主要成分,且這些化合物顯著促進了小鼠的活動,因此被確定為羅馬洋甘菊精油(CHA)的主要活性成分。研究中也顯示活性成分與神經傳遞物質多巴胺相似。
|原料認證
欲取得相關認證資料請 點我加入官方LINE@
▎參考文獻
- Zsolt Sándor1,el. Evidence Supports Tradition: The in Vitro Effects of Roman Chamomile on Smooth Muscles. Published online 2018 Apr 6.
- Toyoshi Umezu.Identification of isobutyl angelate, isoamyl angelate and 2‐methylbutyl isobutyrate as active constituents in Roman chamomile essential oil that promotes mouse ambulation.
- EMA-HMPC (2012). Community Herbal Monograph on Chamaemelum nobile (L.) All., Flos. London: EMA-HMPC.
- Kazemian H1, Ghafourian S1, Heidari H2. Antibacterial, anti-swarming and anti-biofilm formation activities of Chamaemelum nobile against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2015 Jul-Aug;48(4):432-6.
- Menendez-Baceta G., Aceituno-Mata L., Molina M., Reyes-García V., Tardío J., Pardo-de-Santayana M. (2014). Medicinal plants traditionally used in the northwest of the Basque Country (Biscay and Alava), Iberian Peninsula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 152 .113–134.
- Alarcün R., Pardo-de-Santayana M., Priestley C., Morales R. (2015). Author’s accepted manuscript. J. Ethnopharmacol. 176. 207–224.
- Janmejai K Srivastava,1,2,* Eswar Shankar,1,2 and Sanjay Gupta1,2, Chamomile: A herbal medicine of the past with bright future. Mol Med Report. 2010 Nov 1; 3(6): 895– 901.doi: 10.3892/mmr.2010.377
- Essential Oils: A Handbook for Aromatherapy Practice Second Edition. Genus Anthemis Anthemis Nobilis(Also Known As Chaemamelum Nobile)-Roman Chamomile.145-146
- Hernández-Ceruelos A., Madrigal-Santillán E., Morales-González JA, Chamorro-Cevallos G., Cassani-Galindo M., Madrigal-Bujaidar E. (2010). Antigenotoxic effect of Chamomilla recutita (L.) rauschert essential oil in mouse spermatogonial cells, and determination of its antioxidant capacity in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 11:3793–3802.
- Zeggwagh N. A., Moufid A., Michel J. B., Eddouks M. (2009). Hypotensive effect of Chamaemelum nobile aqueous extract in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 31: 440–450.
- Effect of the Internal and External Factors on Yield and Qualitative-Quantitative Characteristics of Chamomile Essential Oil. Acta horticulturae: June 2007, Volume: 749
- Adams R. P. (2007). Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy.
- Barthó L., Benkó R., Patacchini R., Pethö G., Holzer-Petsche U., Holzer P., et al. (2004). Effects of capsaicin on visceral smooth muscle: a valuable tool for sensory neurotransmitter identification . Eur. J. Pharmacol. 500: 143–157.
- Antonelli A., Fabbri C. (1998). Study on Roman chamomile Chamaemelum nobile L. all. oil. J. Essent. Oil Res. 10: 571–574.
- Melegari M., Albasini A., Pecorari P., Vampa G., Rinaldi M., Rossi T., et al. (1988). Chemical characteristics and pharmacological properties of the essential oils of Anthemis nobilis. Fitoterapia 59: 449 –455.
- Abou-Zied E., Rizk A. (1973). Phytochemical investigation of Anthemis nobilis L. growing in Egypt. Qual. Plant. Mater. Veg. 2: 141–144.
- Augustin B., Javorka S., Giovannini R. R. P. (1948). Magyar Gyógynövények [Hungarian Herbal Drugs. New Delhi: Ministry of Agriculture, 299–300.
|部分圖片來自網路,若有侵權請聯繫刪除|