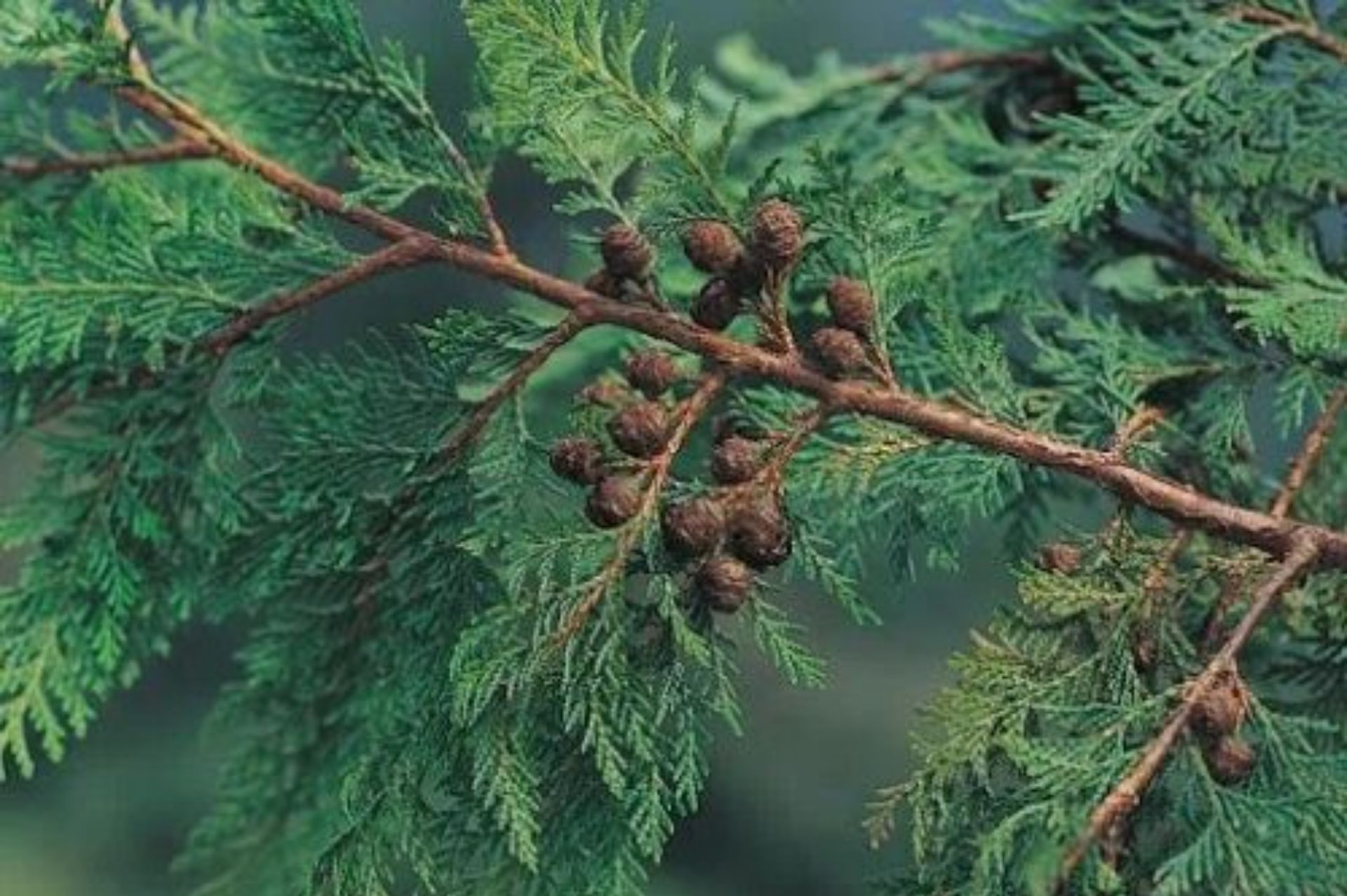
紅檜 Taiwan Benihi (Hinoki)
拉丁學名|Chamaecyparis formosensis
主要產地|台灣
原料分類|木質系列
原料規格|500g-25kg 詳情請洽業務
萃取部位|木材
萃取方式|低溫蒸餾
植物科別|柏科,扁柏屬
植物氣味|木質幽香味,具清爽木脂香氣
▎精油簡介
優選產自台灣高山,檜木主要分佈在海拔1500公尺至2500公尺之間的山地,檜木於冰河時期時落腳於台灣,由於台灣提供相當優異的生長緯度與地理環境,造就了質地優越檜木生態與品質,也讓如此珍貴的木材得以保存。
第一批被發現的紅檜標本被運往東京,於 1901 年正式命名為台灣紅檜。台灣紅檜與日本花柏(Chamaecyparis pisifera)為近緣種,在早期都擁有大量的原始林,後因砍伐而產量大減,因此非常珍貴。
台灣檜木為台灣特別的種類,樹乾皮平滑而薄,木材無辣味,常用於高級建築及家具建材。
▎成分解析
|主要成分:倍半萜醇
台灣檜木的檜木醇(Hinokitiol)含量為特別高,其自然散發的檜木醇香味能夠舒緩緊張的情緒與壓力。目前,世界珍貴的台灣檜木已經越來越少了,而樹體所分泌的檜木醇能保護自己不受蟲蛀與病害的侵襲,故能存活千年以上,而成為人稱的神木。
枝幹萃取的檜木精油以倍半萜醇類為主,針葉萃取的則以單萜烯類為主。另外還有其他成分,如:桃金孃醇(myrtenol)、桃金孃醛(myrtenyl)、γ-杜松烯(g-cadiene)、松油萜、樟烯、對繖花烴、萜烯醇、樟腦等。
|成分:Hinokitiol
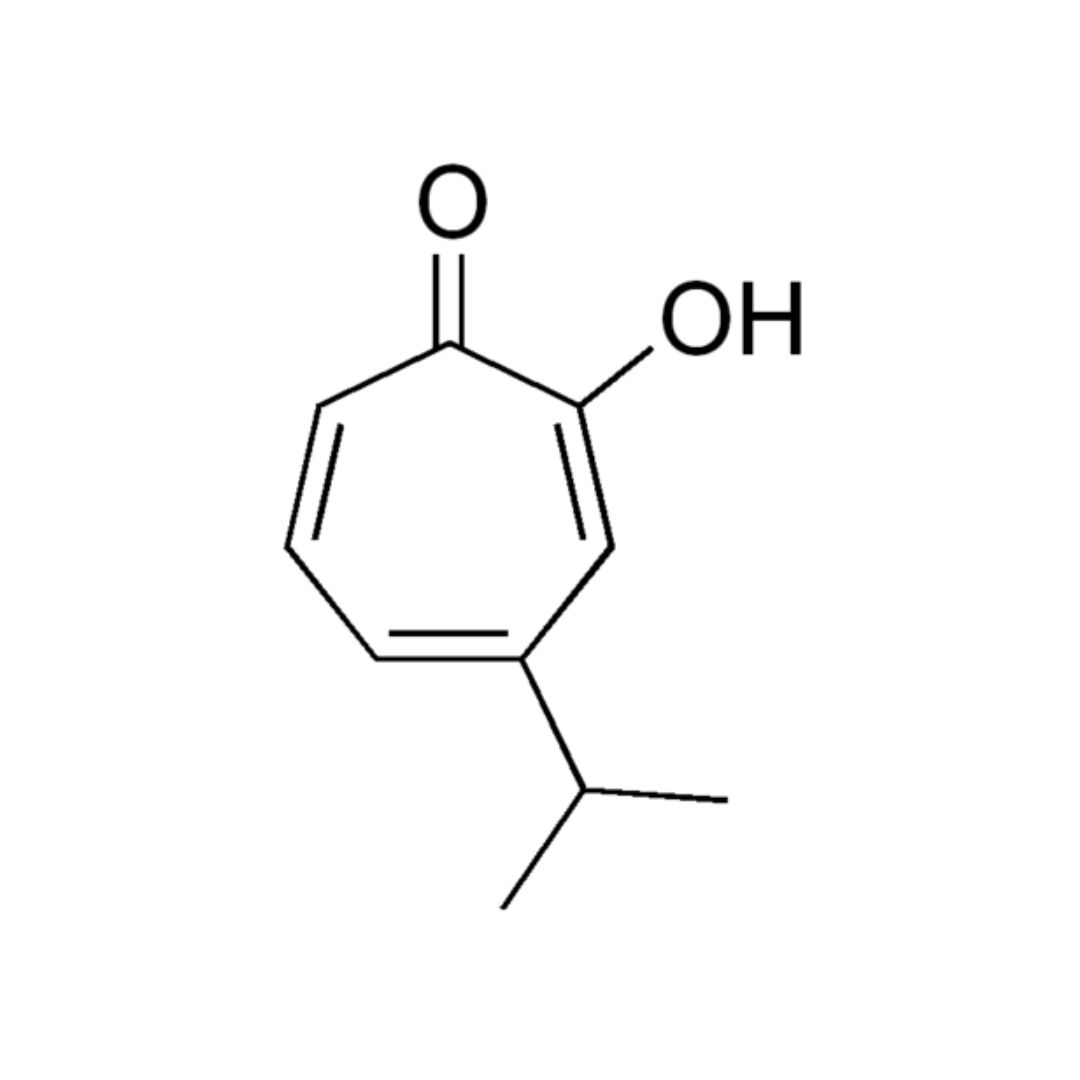
▸ 台灣檜木的檜木醇(Hinokitiol)含量為特別高。
|研究認證

▸ 顯示扁柏酚在血管平滑肌細胞(VSMC)中相關的研究。
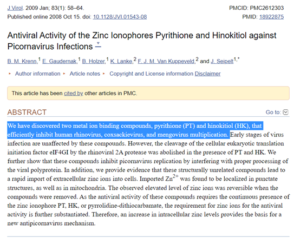
▸ 近期的研究表明,Hinokitiol與鋅化合物聯合使用時,對於多種人類病毒(包括鼻病毒,柯薩奇病毒和芒果病毒)的相關研究。

▸ 其成分目前在德、日、美等國家已被廣泛應用於醫藥品、化妝品、食用品等。
|原料認證
欲取得相關認證資料請 點我加入官方LINE@
▎參考文獻
- Chedgy R(2010). Secondary metabolites of Western red cedar (Thuja plicata): their biotechnological applications and role in conferring natural durability. LAPLambert Academic Publishing. ISBN 978-3-8383-4661-8.
- Secretariat,Treasury Board of Canada; Secretariat, Treasury Board of Canada. "Detailedcategorization results of the Domestic Substances List - Open Government Portal". open.canada.ca. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- Grillo AS, SantaMaria AM, Kafina MD, Cioffi AG, Huston NC, Han M, et al. (May 2017). "Restorediron transport by a small molecule promotes absorption and hemoglobinization inanimals". Science. 356 (6338): 608 –616.
- Service RF (May2017). "Iron Man molecule restores balance tocells". Science Magazine. AAAS. Retrieved 2020-05-20.
5. Mechanism of the Inhibitory Effect of Hinokitiol on Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation Dissertation, Taipei Medical University Institute of Medical Sciences; 2010 (2010 / 01 / 01), P1 – 81 - Mechanism of the Inhibitory Effect of Hinokitiol on Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation Dissertation, Taipei Medical University Institute of Medical Sciences; 2010 (2010 / 01 / 01), P1 – 81
- Inhibitory effect of PDGF-BB and serum-stimulated responses in vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by hinokitiol via up-regulation of p21 and p53. April 2018 Archives of Medical Science 14(3):579-587
- IP Australia: AusPat". Australian Government - Intellectual Property Australia. Retrieved 2020-05-20
- Shih YH, Chang KW, Hsia SM, Yu CC, Fuh LJ, Chi TY, Shieh TM (June 2013). "In vitroantimicrobial and anticancer potential of hinokitiol against oral pathogens and oral cancer cell lines". Microbiological Research. 168 (5 ): 254–62.
- Morita Y, SakagamiY, Okabe T, Ohe T, Inamori Y, Ishida N (September 2007). "The mechanism of the bacterial activity of hinokitiol". Biocontrol Science. 12 (3):101–10
10.Wang TH, Hsia SM, WuCH, Ko SY, Chen MY, Shih YH, et al. (2016-09-28). "Evaluation of the Antibacterial Potential of Liquid and Vapor Phase Phenolic Essential Oil Compounds against Oral Microorganisms". PloS One . 11 (9): e0163147. - Jayakumar T, Liu CH, Wu GY, Lee TY, Manubolu M, Hsieh CY, et al. (March 2018). "Hinokitiol Inhibits Migration of A549 Lung Cancer Cells via Suppression of MMPs and Induction of Antioxidant Enzymes and Apoptosis". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19 (4).
- Krenn BM, GaudernakE, Holzer B, Lanke K, Van Kuppeveld FJ, Seipelt J (January 2009). "Antiviral activity of the zinc ionophores pyrithione and hinokitiola against picornavirus infections". Journal of Virology. 83 (1): 58–64 .
|部分圖片來自網路,若有侵權請聯繫刪除|